Nouns
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. It serves as the fundamental building block of sentences, providing the subject or object around which language revolves. Nouns can be concrete, like “dog” or “house,” which are tangible and observable, or abstract, such as “love” or “justice,” representing concepts or qualities. Learning nouns in English is crucial because they form the backbone of communication. They allow individuals to name and reference the people, objects, and concepts in their surroundings, facilitating clear and effective expression. Understanding nouns helps learners construct grammatically correct sentences, enabling them to convey ideas accurately and succinctly. Moreover, mastering nouns lays the groundwork for comprehending more complex grammatical structures and advancing language proficiency in reading, writing, and speaking English.
Pronouns
Pronouns are words used in place of nouns to avoid repetition or to refer back to a previously mentioned noun. They streamline language by replacing specific nouns with more general terms like “he,” “she,” “it,” “they,” “we,” and “you.” Pronouns benefit learning English by making communication more efficient and concise. They simplify sentence structure, enhance readability, and encourage fluency by allowing speakers and writers to convey ideas without constant repetition of nouns. Moreover, mastering pronouns helps learners understand sentence cohesion and develop a deeper understanding of grammar rules, leading to improved writing and speaking skills in English.
Verbs
A verb is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being in a sentence. It’s like the engine that drives the sentence forward. Verbs show what someone or something does (e.g., “run,” “jump”), what happens (e.g., “rain,” “grow”), or describe a state of being (e.g., “is,” “was”). They are essential for conveying actions, events, or conditions in communication. Verbs can also indicate tense, showing when an action occurs (e.g., present, past, future). In essence, verbs are the action words that give life and movement to sentences, allowing us to express a wide range of thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
Adjectives
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun by providing more information about its qualities or characteristics. Adjectives add color, detail, and precision to language, helping to create vivid and nuanced descriptions. They answer questions like “What kind?” “Which one?” or “How many?” Adjectives benefit learning English by enabling learners to express themselves more precisely and vividly. They enhance vocabulary, encouraging the use of descriptive language. Mastering adjectives enhances writing and speaking skills, allowing learners to paint a clearer picture and evoke stronger emotions. Understanding adjectives fosters effective communication and fosters appreciation for the richness of language.
Adverbs
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb, providing information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens. Adverbs add depth and clarity to language, enhancing the precision and expressiveness of communication. They answer questions like “How?” “When?” “Where?” or “To what degree?” Adverbs benefit learning English by enabling learners to convey a wide range of meanings and nuances in their writing and speech. They help to refine and expand vocabulary, encouraging learners to express themselves with greater specificity and accuracy. Mastering adverbs fosters clearer communication and enhances overall language proficiency.
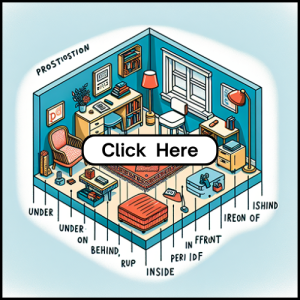
Prepositions
A preposition is a word that helps describe the relationship between two things in a sentence.
It usually shows the position of something in space or time. For example, in the sentence “The book is on the table,” the word “on” is a preposition because it shows the position of the book in relation to the table.
Common prepositions include words like “in,” “under,” “over,” “between,” and “behind.”
Prepositions are essential for giving more detailed information about how things are connected in a sentence. They often come before a noun or pronoun, forming a prepositional phrase that adds context to the sentence. Understanding prepositions is important for learning English as they help clarify the relationships between words and provide a more complete picture of the language’s structure.
Conjunctions
A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence, allowing for smoother and more coherent communication. Common conjunctions include “and,” “but,” “or,” “so,” “for,” and “yet.” Conjunctions benefit learning English by facilitating the formation of complex sentences and expressing relationships between different ideas or elements. They help learners construct compound and complex sentences, enabling them to convey more nuanced thoughts and connect related concepts. By mastering conjunctions, learners can improve their ability to organize ideas logically, leading to clearer and more structured writing and speech in English.
Interjections
An interjection is a part of speech that expresses sudden emotions or feelings in a sentence. It is like a short burst of expression that can stand alone or appear within a sentence and is usually followed by an exclamation mark or comma. Interjections add color and emotion to our language, showing joy, surprise, excitement, or other strong feelings.
For example, “Wow!” and “Oops!” are common interjections that convey surprise and mild distress, respectively. They can help make conversations more animated and engaging by providing a direct way to express our immediate reactions. By understanding how interjections work, learners can better grasp the nuances of emotional expression in the English language.